Quinine induced thrombotic microangiopathy and thrombocytopenia: A teaching hospital's perspective
Main Article Content
Abstract
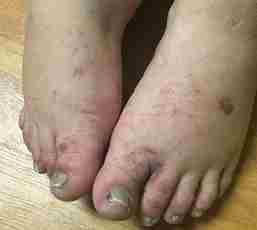
Although quinine is an infrequently prescribed drug, with malaria treatment being its only FDA-approved indication, unwitting exposure via beverages (e.g., tonic water), over the counter herbal remedies and illegal recreation drugs still occur. We present a unique case of a female patient who denied any known prior history of quinine exposure, who after being prescribed quinine tablets for restless leg syndrome, developed an immune-related thrombotic microangiopathy with thrombocytopenia and subsequent multi-organ failure. It was later elucidated that her only known potential source of prior quinine exposure was a remote history of crack-cocaine use. The patient survived this rare and severe inflammatory response with recovery of renal function and was able to discontinue dialysis.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
- George JN and CM Nester. Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. New England Journal of Medicine, 2014, 371(7): 654-66.https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1410951
- Reese JA, Bougie DW, Curtis BR, et al. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: Experience of the Oklahoma registry and the Blood Center of Wisconsin. American Journal of Hematology, 2015, 90(5): 406-410.https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.23960
- Aster RH and DW Bougie. Drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia. New England Journal of Medicine, 2007, 357(6): 580-587.https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra066469
- Vipan WH. Quinine as a cause of purpura. The Lancet, 1865, 86(2184): 37.
- Al-Nouri ZL, Reese JA, Terrell DR, et al. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: a systemic review of published reports. Blood, 2015, 125(4): 616-618.https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-11-611335
- Winter FD. Immune thrombocytopenia associated with consumption of tonic water. Proceedings (Baylor University Medical Center), 2015, 28(2): 213.
- Liles NW, Page EE, Liles AL, et al. Diversity and severity of adverse reactions to quinine: a systematic review. American Journal of Hematology, 2016, 91(5): 461-466.https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.24314
- George JN, Morton JM, Liles NW, et al. After the Party’s Over. New England Journal of Medicine, 2017, 376(1): 74-80.https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcps1606750
- Lim A, Ho L and V Levidiotis. Quinine-induced renal failure as a result of rhabdomyolysis, haemolytic uraemic syndrome and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Internal Medicine Journal, 2006, 36(7): 465-67.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1445-5994.2006.01104.x